Amar has been a pioneer, largest manufacturer, and exporter of continuous flow reactors in India since many years. Amar Flow reactors are used by various industries like fine & speciality chemicals, bulk drugs (API) pharmaceuticals, dyes, intermediates, paints, agrochemicals, etc. to convert their batch chemistries to continuous flow.
Microreactors are one of the most talked about innovations in the process development laboratory in the last decade. In spite of widespread publications, industrial adoption can be sometimes slow. R&D Teams struggle to justify return on investment and here we try to provide some tips that have helped our customers select the best chemistry scenarios to deploy a microreactor in.
Highly Exothermic reactions: Typically, as a reactor becomes larger the surface area to volume ratio decreases. As a result, it is exceedingly difficult to conduct reactions which have large exotherms in conventional reactors. Our Amar microreactors are an excellent option for conducting such reactions for multiple reasons:
Large heat transfer surface areas
Safety impact is limited due to small reactant holdups
Toxic or corrosive reagents: In Pharma or specialty chemicals R&D teams can be wary to use synthesis that includes corrosive, toxic, or pyrophoric reagents. Microreactors are a safe option since in the worst-case scenario very limited exposures would happen. For synthesis using low LD50 value chemicals always consider a flow synthesis in a microreactor due to enhanced safety. Talk to our experts at Amar to find out exotic MOC options such as Hastealloy for your reaction requirements.
Process intensification: Customers can be disappointed due to the high costs of microreactors relative to throughput (kilos per day) especially in production scenarios. One mistake we see customers make is to use the same T or P conditions that they have been using in batch reactors in the plant. Microreactors are usually capable of withstanding much more aggressive T and P conditions. Such conditions can give faster reactions and hence justify the higher costs of a microreactor per unit volume. Be willing to experiment to find the best T and P for selectivity and throughput and often this will lead to more aggressing operating points of T and P.
Batch to continuous conversion: Often the first part of this process is to evaluate reaction kinetics. Microreactors can be an excellent way to collect such data rapidly without wasting expensive reagents. Furthermore, due to higher mixing and heat transfer, it is easier to obtain inherent reaction kinetics and not get misleading results due to heat transfer limits or mass transfer limits
Lab scale Synthesis of new molecules: In the initial stages of new molecules or impurities milligram or microgram quantities are often sufficient. However in a conventional lab synthesis, larger quantities must be made, and this wastes resources. A cascading synthesis in flow mode with microreactors can very often be the perfect match for such demands.
Prioritizing intermolecular reactions versus an intramolecular product: Some chemical synthesis have competing intermolecular versus intramolecular products. In conventional macro-scale reactor processes it becomes impossible to get the intermolecular product at high selectivity since the kinetics favours the intramolecular product. However, since microreactors have low mixing distances they can often be used to tune selectivity towards the desired intermolecular product.
This should provide customers some food for thought about use cases where microreactors would be a great match for their projects. Do talk to our experts at Amar [email protected] for additional assistance in deciding whether a microreactor or a conventional reactor would work best for their requirements.
Also, check out our products Continuous Stirred Tank Reactor and Tubular Reactor with Static Mixer
Read Best Use Cases For Microreactors to know more about these tips.
| Model | AMaR 2 - 12 |
|---|---|
| Volume ( ml ) | 12 |
| Flow Rate* ( lph ) | Up to 43 |
| Heat Transfer Area (m2 / m3) | ~ 2000 |
| Design Pressure ( bar ) | 20 |
| Design Temperature ( °C ) | - 50 to 200 |
| Material of Construction | SS-316 / Hastelloy C 276 |
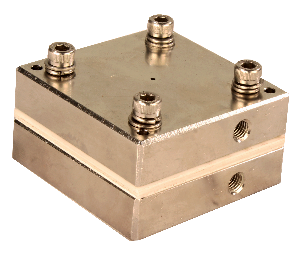
| Multiple Plates | Up to 10 plates can be connected in series or parallel to give volume up to 2 litres |
| Accessories | Pressure Gauge, Pressure Safety Valve |
Note : * Assuming 1 sec as residence time – actual flow rate may vary for application.
| Model | AMaR 2 - 50 |
|---|---|
| Volume ( ml ) | 50 |
| Flow Rate* ( lph ) | Up to 180 |
| Heat Transfer Area (m2 / m3) | ~ 1700 |
| Design Pressure ( bar ) | 20 |
| Design Temperature ( °C ) | - 50 to 200 |
| Material of Construction | SS-316 / Hastelloy C 276 |
| Multiple Plates | Up to 10 plates can be connected in series or parallel to give volume up to 2 litres. |
| Accessories | Pressure Gauge, Pressure Safety Valve |
Note : * Assuming 1 sec as residence time – actual flow rate may vary for application.
| Model | AMaR 2 - 200 |
|---|---|
| Volume ( ml ) | 200 |
| Flow Rate* ( lph ) | Up to 720 |
| Heat Transfer Area (m2 / m3) | ~ 1100 |
| Design Pressure ( bar ) | 20 |
| Design Temperature ( °C ) | - 50 to 200 |
| Material of Construction | SS-316 / Hastelloy C 276 |
| Multiple Plates | Up to 10 plates can be connected in series or parallel to give volume up to 2 litres. |
| Accessories | Pressure Gauge, Pressure Safety Valve |
Note : * Assuming 1 sec as residence time – actual flow rate may vary for application.
Apart from our standard specifications we also provide additional value-added optional accessories to enhance the versatility and functionality of the equipment for various applications. Some of the components that we provide as a part of our flow reactor systems :
It is SS316 regulator mounted on the vent line of the reactor &is used for maintaining constant pressure inside the reactor up to 350bar. The pressure is maintained by releasing the excess pressure into the atmosphere.
Optional
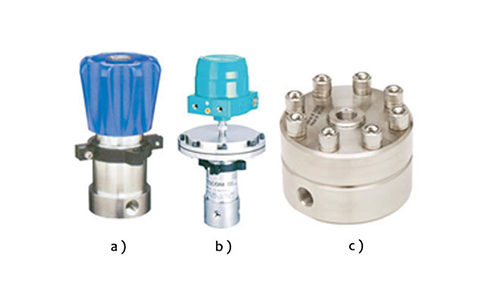
Control Panel consists of programmable PID temperature controller cum indicator with temperature alarm system (settable), safety alarm & heater trip system for malfunctioning of controller/sensor/ temperature rise beyond set limit. Digital pressure indicator/ controller, gas/liquid flow indicator, totalizer, heater, level, pH etc. Indicators are provided additionally on same common control panel depending on the optional accessories are selected.
Optional :


It consists of SS316 pressure sensor (transmitter) & digital pressure indicator/ controller (mounted on common control panel) with pressure alarm.

This unit is used to separate plug flow of two immiscible liquids used in biphasic reaction or two phases of an extraction flow.
MOC: ETFE, PFA & PTFE, pressure @ 300 psi.
This system is used to charge liquid at a desired rate from as low as 1ml/hr, is under pressurized condition.

MFM can be used to measure accurate mass flow rate of gas (in gm/hr or LPH) & totalized quantity of mass/volume (in gm/ltr) charged in the reactor at any point. Mass flow controller (MFC) is used to charge the set flow rate of gas into the reactor at high pressures up to 100bar. The same MFM/MFC comes with high pressure flexible hose, inlet filter with digital gas flow indicator.

Note : All accessories may not be applicable for the selected model. For more details Contact US.
All wetted parts are made from SS-316L / SS-316 as standard.
Optional: Hastelloy B/C, Titanium, Monel, Inconel, Zirconium, Tantalum, Carbon Steel, etc. for different liquids corrosive to SS-316. Other special alloys like A286, Alloy 20, duplex steel, etc. can also be offered.
Note: Amar offers all the internal & optionally external wetted pats in the same material of construction as that of body & head to give fully corrosion resistant autoclaves.
Material Selection Guide: AMAR gives recommendation for material selection for particular media, however it does not guarantee 100% corrosion resistance of a particular material to a particular corrosive media, as the same depends on various parameters like temperature, pressure, concentration, etc. of the reactions. Reactor vessels of material SS316, above 5 ltr are normally fabricated from plates. SS 316 autoclaves up to 100 ltr have lids made from rolled / forged bar stock. The material listed below may not be available in all possible sizes.
SS316 is an alloy of chromium – nickel with molybdenum which improves the corrosion resistance properties. The molybdenum in the material also elevates its strength. SS 316 / 316L both have almost the same corrosion resistance properties, the only difference is SS 316L has a low carbon stainless steel content.
SS 316 / 316L has excellent corrosion resistance to:
SS316 / 316L has poor resistance to:
Applications of SS 316 / 316L is mainly in chemical & petrochemical industry, food processing, pharmaceutical equipment, & also in marine & architectural applications.
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Iron ( Fe ) | 60% - 67% |
| Nickel ( Ni ) | 9% - 12% |
| Chromium ( Cr ) | 18% - 21% |
| Molybdenum ( Mo ) | 2% - 3% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.08% |
| Other: | |
| Silicon ( Si ) | 2% |
| Manganese ( Mn ) | 1.5% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| SS 316 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 2 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature shall depend on the corresponding pressure requirement.
Hastelloy C22, also known as Alloy C22, is a superalloy of nickel-chromium-molybdenum with a chemical composition of nickel 56%, chromium 22% & molybdenum 13% along with a substantial amount of iron, cobalt & tungsten. Hastelloy C22 has the widest corrosion resistance & is the most widely used alloy for corrosion media.
Hastelloy C22 has excellent corrosion resistance to:
Hastelloy C22 possess the following properties:
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Chromium ( Cr ) | 20% -22.5% |
| Molybdenum ( Mo ) | 12.5% - 14.5% |
| Tungsten ( W ) | 2.5% - 3.5% |
| Cobalt ( Co ) | 2% - 6% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | 0.08% |
| Other: | |
| Manganese ( Mn ) | 0.5% |
| Vanadium ( V ) | 0.35% |
| Silicon ( Si ) | 0.08% |
| Phosphorous ( P ) | 0.02% |
| Sulphur ( S ) | 0.02% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.015% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Alloy C22 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature shall depend on the corresponding pressure requirement.
Hastelloy C-276, also known as Alloy C276, is a nickel-molybdenum-chromium alloy with a trace quantity of tungsten that has been reinforced by solid solution. Excellent corrosion resistance is displayed by Alloy C-276 in a number of challenging environments and media. It is ductile, readily made, and weldable, like many other nickel alloys. Most industrial applications where there are special chemical environments and other alloys have failed adopt this alloy.
Applications:
The manufacturing of pulp and paper, oil and gas, electricity generation, pharmaceutical, chemical and petrochemical processing, and waste water treatment are just a few of the industries that regularly use Hastelloy C-276. Stack liners, ducts, dampers, scrubbers, stack gas reheaters, heat exchangers, reaction vessels, evaporators, transfer pipework, and several more extremely corrosive applications are examples of end use applications.
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Nickel ( Ni ) | 55% - 63% |
| Molybdenum ( Mo ) | 15% - 17% |
| Chromium ( Cr ) | 14.5% - 16.5% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | 4% - 7% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.01% |
| Other: | |
| Cobalt ( Co ) | 2.5% |
| Tungsten ( W ) | 3% - 4.5% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Alloy C276 | 5 | 6 | 5 | 6 | 4 | 6 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature shall depend on the corresponding pressure requirement.
A nickel-copper alloy called Monel 400, constituting 67% Ni & 23% Cu, is resistant to salt and caustic solutions, as well as sea water and steam at high temperatures. The only way to harden Monel 400 is through cold working because it is a solid solution alloy. High strength, outstanding weldability, and strong corrosion resistance are all features of this nickel alloy.
Monel 400 offers excellent corrosion resistance to:
Monel 400 has poor resistance to nitric acid & ammonia systems.
It has varied applications in marine engineering, chemical & hydrocarbon processing equipment, crude petroleum stills, etc.
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Nickel ( Ni ) | 65% |
| Copper ( Cu ) | 30% |
| Aluminium ( Al ) | 2.3% - 3.1% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | 2% |
| Other: | |
| Titanium ( Ti ) | 0.35%-0.85% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.3% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Alloy 400 | 5 | 6 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 3 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature: 482°C
Inconel 600 / 625 is a nickel–chromium non-magnetic high temperature alloy that offers excellent properties of high strength & corrosion & heat resistance. Due to its high nickel concentration, the alloy is essentially impervious to chloride-ion tress-corrosion cracking and resistant to both organic and inorganic compound corrosion. Chromium offers resistance to oxidizing onditions in corrosive solutions or at high temperatures, as well as resistance to Sulphur compounds. Inconel 600 / 625 can only be strengthened and hardened through cold work; precipitation hardening is not an option. Due to INCONEL alloy 600's adaptability, it is used in a wide range of applications including temperature.
It offers excellent resistance to:
Chemical Composition of Inconel 600:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Nickel ( Ni ) | 73% - 80% |
| Chromium ( Cr ) | 14% - 17% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | 2% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.15% |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature: 482°C
Chemical Composition of Inconel 625:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Nickel ( Ni ) | 58% |
| Chromium ( Cr ) | 22% - 23% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | 8% - 10% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.15% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Alloy 600/625 | 3 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 3 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 5 | 3 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature shall depend on the corresponding pressure requirement.
One of the strongest metals in use is nickel 200, a 99.6% pure nickel alloy. It has strong thermal and electrical conductivity as well as outstanding mechanical qualities. Additionally, Nickel 200 is highly resistant to corrosive environments and is simple to fabricate because to its advantageous features and chemical makeup. Nickel 200 sustains the majority of corrosive and caustic conditions, media, alkalis, and acids with exceptional durability (sulfuric, hydrochloric, hydrofluoric). Ni 200, which is applied indoors and outdoors, also has:
It offers high resistance to:
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Nickel ( Ni ) | 99.4% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | 0.4% |
| Carbon ( C ) | 0.15% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Nickel 200 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 2 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature: 316°C
Commercially pure titanium is available in grades 2 and 4 (at least 99% titanium). The chemical makeup of each grade varies somewhat, which has an impact on mechanical qualities and design potential. Both grades share a similar level of corrosion resistance. Titanium is very corrosion resistant, lightweight, and frequently outperforms stainless steels in most conditions in terms of corrosion resistance. Grade 2 is the preferred alloy for the majority of industrial applications that call for good ductility and corrosion resistance out of the four commercially pure (C.P.) titanium grades.
It has excellent corrosion resistance to:
Titanium alloys are used extensively in the medical and aerospace industries. Titanium Grade 2 is highly suited for use in the marine, chemical processing, and desalination industries due to its strength and corrosion resistance. Applications for Grade 2 titanium often include flue-gas desulphurization systems, reaction and pressure vessels, heat exchangers, liners, tubing or piping systems, oil and gas components, and many other industrial parts. Temperatures for continuous service can reach up to 800°F, and for sporadic, intermittent service, they can reach up to 1000°F.
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Titanium ( Ti ) | >=98.9% |
| Iron ( Fe ) | <=0.4% |
| Oxygen ( O ) | <=0.25% |
| Carbon ( C ) | <=0.08% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Titanium | 3 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 0 | 1 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature: 316°C
Zirconium 702 has excellent thermal conductivity, corrosion resistant, and is inert to all organic and inorganic substances. Its qualities make it the perfect substance for corrosion-resistant process equipment. Any piece of process equipment where corrosion is a concern should be given zirconium consideration due to its long-term advantages of decreased downtime, greater life expectancy, and profitability.
Zirconium is widely recognized for its resistance to pitting and crevice corrosion as well as its immunity to stress corrosion cracking. At ambient temperature, a protective oxide layer forms on this reactive metal because of its high affinity for oxygen.
Zirconium offers excellent corrosion resistance to:
It has poor resistance to oxidizing agents
Chemical Composition:
| Element | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Zirconium ( Zr ) | 95.5% |
| Hafnium ( Hf ) | 4.5% |
| Iron ( Fe ) + Chromium ( Cr ) | 0.2% |
| Nitrogen | 0.025% |
Corrosion Rating:
RATINGS - 0:Unsuitable 1:Poor to Fair 2:Fair 3:Fair to good 4:Good 5:Good to Excellent 6:Normally Excellent
| Materials | Non-oxidizing or reducing media | Liquids | Gases | |||||||
| Acid solutions excluding Hydrochloric, phosphoric, sulfuric | Neutral solutions, e.g. many Non-oxidizing salt solutions, chlorides, sulfates | Alkaline solutions | Oxidizing Media | Halogen & derivatives | ||||||
| Caustic & mild alkalis, excluding ammonium hydroxide | Ammonium hydroxide & amines | Acid solutions, e.g. nitric | Neutral or alkaline solutions e.g. per sulfates, peroxides, chromates | Pitting media, acid ferric chloride solutions | Halogen | Hydrogen halides, dry, e.g., dry, hydrogen chloride | ||||
| Moist, e.g. chlorine below dew point | Dry, e.g. fluorine above dew point | |||||||||
| Zirconium | 3 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 6 | 6 | 2 | 6 | 1 | 6 |
Note: Maximum Design Temperature: 316°C
Tantalum is practically inert to many oxidizing & reducing acids. It offers the best & most outstanding resistance to wide variety of corrosive media including hydrochloric acid. It is attacked by hot alkalis & hydrofluoric acid.
Note: Maximum Design Temperature: 371°C